|
The market can be in two modes: cycle and trend. In the cycle mode the cost of the currency pair oscillates around some value. In another words, if the cost goes up during some time, it will go down by an equivalent value. In the trend mode, the cost of the pair will go up or go down persistently during relatively long time. Some strategies can be used only if market is in the trend mode, another - only if the market is in the cycle mode. For example, if the market is in up trend one needs to buy, if in down trend – sell.
Trend mode indicator shows us the mode of the market. If the indicator value is 1, the market is in the trend mode, if 0 – in the cycle mode. To illustrate it, consider the picture bellow. If the market in the trend mode, we see a stable increase("trend 1") or a decrease("trend 2") value of the currency pair. If the market is in the cycle mode, we see that the value of the currency pair cost does oscillate.
In order to calculate the trend mode, first one needs to calculate the current phase(The theory behind the calculations is too elaborated, for further reference see the following sources :”Cybernetic Analysis for Stocks and Futures: Cutting-Edge DSP Technology to Improve Your Trading (Wiley Trading)" and Rocket science for traders by John F. Ehlers. For understanding of mathematical aspects, see "Random Data. Analysis and measurements procedure" by J.S. Bendat & A.G. Piersol ). In order_ to understand meaning of this value please consider the angle of _the sinevave. The phase is the angle of the periodical oscilation. The phasor is a vector with the start in the point of origin and the end in the measurement point. InPhase is projection of the phasor on abscissa, Quadrature - the projection on the ordinate
The Current Phase is calculated as an arctan of the Quadrature/InPhase value
Phase = Arctan(Quadrature/InPhase)
Then calculate the dominant cycle period
Then sum phases during the dominant cycle period
If sum of phase has not changed or has changed gradually, the market in the trend mode, if it changed swiftly – in the cycle mode
Algorim of calculations
1) Calculate weighted moving average for last five bars and push it in array smooth
smooth=(4*price[0]+3*price[1]+2*price[2]+price[3])/10;
2) Caclulate detrender for last 6 bars Detrender=(0.0962*Smooth[0]+0.5769*smooth[2]-0.5769*smooth[4]-0.0962*Smooth[6]);
3) Multiply detrender on value (0.075+Period[1]+0.54) where Period[1] – period values calculated on previous iteration. If there was not iteration before, Period[1] equals to zero.
4) Add detrender to appropriate array
5) Compute in-phase and quadrature component. Push values in appropriated arrays. Q1=(0.0962*detrender[0]+0.5769*Detrender[2]-0.5769*Detrender[4]-0.0962*Detrender[6])*(0.075*Period[1] +0.54);
I1=Detrender[3];
6) Advance the phase of in_phase and quadrature components by 90 degrees
jI=(0.0962*I1[0]+0.5769*I1[2]-0.5769*I1[4]-0.0962*I1[6])*(0.075*Period[1] +0.54)
jQ=(0.0962*Q1[0]+0.5769*Q1[2]-0.5769*Q1[4]-0.0962*Q1[6])*(0.075*Period[1] +0.54)
7) Calculate I2 and Q2 values
I2=I1+jQ
Q2=Q1+jI
8) Smooth the I and Q compponents before applying
I2 =0.2*I2+0.8*I2
Q2=0.2*Q2+0.8*Q2
9) Push I2 and Q2 values in appropriate arrays
10) Calculate real and imagine part of vector
Re=I2[0]*I2[1]+Q2[0]*Q2[1]
Im=I2[0]*Q2[1]-Q2[0]*I2[1]
where I2/Q2[0] - value of current bar, I2/Q2[1] – value of previous bar (if there was not previous iteration I2[1] and Q2[1] equals to zero)
11) Smooth real and imagine part of vector.
Re=0.2*Re+0.8*Re[1];
Im=0.2*Im+0.8*Im[1];
12) Push it to appropriate array
13) If Imagine and real part of vector not equal to zero, then Period = 360/arctan(imagine/real) else period =0;
14) Smooth period period= 0.2*Period+ 0.8Period[1] Where Period[1] – value of previous bar
15) SmoothPeriod= 0.33*Period +0.67*SmoothPeriod[1], SmoothPeriod[1] -value of previous bar, if there was not bar before SmoothPeriod[1] equals to zero
16) Push SmoothPeriod to appropriate array
17) Calculate dominant cycle period DCPeriod=round(SmoothPeriod+0.5);
18) Push DCPeriod to appripriate array
19) Calculate sum of image and real part
For count=0 to DCPeriod-1
SumRealPart+=cos(count *360/DCPeriod)*Smooth[price];
SumImagePart+=sin(count *360/DCPeriod)*Smooth[price];
20) If |SumRealPart|>0 DCPhase=Arctan(SumImagePart/SumRealPart)
21) If |SumRealPart|<0.01 DCPahse=90*Sign(ImagePart)
22) DCPhase=DCPhase+90;
23) Compensate for one bar lag of the Weighted Moving Average
DCPhase=DCPhase +360/SmoothPeriod
24) If SumImagePart<0 DCPhase=DCPhase+180
25) If DCPahse>315 DCPhase=DCPhase-360;
26) Push DCPhase to appropriate array
27) Calculate ITrend for last 5 bars and push it to appropriate array
for count=0 to DCPeriod-1
Itrend=ITrend +Price[count]
Where Price[i] value of I – bar
28) If DCPeriod>0 iTrend=ITrend/DCPeriod
29) if current iteration >12
TrendLine = 4*ITrend+3*TTrend[1]+2*ITrend[2]+ITrend[3];
else
TrendLine=Price;
30) Calculate trend mode
31) Trend=0;
32) If Sine(DCPhase) Crosses sine(DSPhase+45)
DaysInTrend=0;
Trend=0;
33) DaysInTrend+=1;
34) If DaysInTrend<0.5SmoothPeriod Trend=0
35) Cycle mode if delta phase is +/- 50% of dominan cycle change of phase
If (SmoothPeriod!=0 and (DCPhase-DCPhase[1])>0.67*360/SmoothPeriod and DCPhase -DCPhase[1]<1.5*360/SmothPeriod)
Trend=0;
36) if (|(Smooth-TrendLine)/TrendLine|>=0.15)
Trend=1;
If Trend =0 that mean market in cycle mode, in other case – trend mode
| Attachments: |
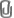 trend_cycle.jpg [221.23 KiB]
trend_cycle.jpg [221.23 KiB]
Downloaded 398 times
|
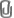 phase.jpg [7.47 KiB]
phase.jpg [7.47 KiB]
Downloaded 379 times
|
|
DISCLAIMER: Dukascopy Bank SA's waiver of responsability - Documents, data or information available on
this webpage may be posted by third parties without Dukascopy Bank SA being obliged to make any control
on their content. Anyone accessing this webpage and downloading or otherwise making use of any document,
data or information found on this webpage shall do it on his/her own risks without any recourse against
Dukascopy Bank SA in relation thereto or for any consequences arising to him/her or any third party from
the use and/or reliance on any document, data or information found on this webpage.
|
|


